What is Artistic Design? Principles, Elements & Creative Techniques
Explore the meaning of artistic design and its key elements like color, form, balance, and composition. Learn how these principles are used in visual and digital design to create impactful art.
Introduction to Artistic Design
- Elements and principles of design
- Color theory and application
- Typography and hierarchy
-
Design thinking process
- Download PDF
Tools:
Module 1: Introduction to Artistic Design
- Elements of Design: Line, shape, color, texture, space, value, form
- Principles of Design: Balance, contrast, emphasis, hierarchy, pattern, rhythm, unity
Module 2: Color theory and application
Color theory and its application
-
Color theory is the study of how humans perceive color and how colors interact with each other. It delves into the science of light and color, the psychology of color perception, and the practical applications of color in various fields.
-
Color theory is like a secret code for understanding colors. It teaches us two things:
- How we see colors: This includes how our eyes and brains work together to make us see all the different colors around us.
- How colors work together: Some colors look good next to each other, while others clash. Color theory helps us pick colors that look great together.
Here are the key aspects of color theory:
1. The Color Wheel
The color wheel is a fundamental tool in color theory. It is a circular diagram that organizes colors based on their relationships to each other. The most common color wheel includes 12 hues:
There are two main types of color wheels used in different contexts:
1. RYB (Red Yellow Blue) Color Model
This is the traditional color wheel used by artists for mixing paints and pigments. The primary colors are red, yellow, and blue.
-
Primary colors: Red, yellow, and blue are the primary colors because they cannot be created by mixing other colors.
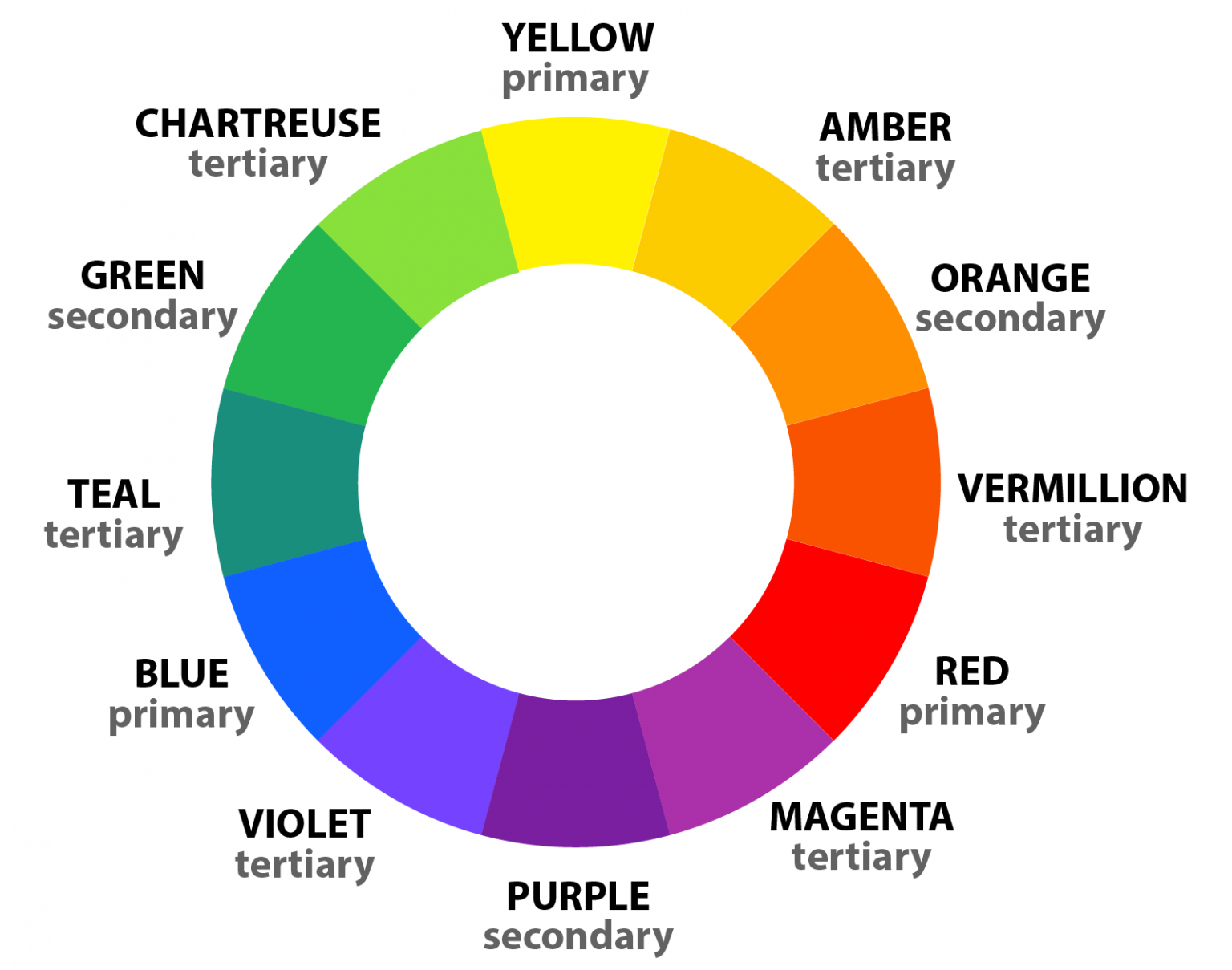 .
Image source: www.color-meanings.com
.
Image source: www.color-meanings.com - Secondary colors: Orange, green, and purple are created by mixing two primary colors in equal proportions. secondary colors are created by mixing any two primary colors. For example, mixing red and yellow creates orange, yellow and blue creates green, and red and blue creates purple.
- Tertiary colors: These are created by mixing a primary and a secondary color. There are six tertiary colors: red-orange, yellow-orange, yellow-green, blue-green, blue-violet, and red-violet.
2. RGB (Red Green Blue) Color Model
- This color wheel is used for light and digital applications such as TVs, computers, and smartphones.
-
The color system that best matches the human eye is the red-green-blue color system.
- Color Wheel Calculator | Canva Colors
- RGB Color Codes Chart
Primary, secondary and tertiary colors [2]
There are 12 main colors on the color wheel. In the RGB color wheel, these hues are red, orange, yellow, chartreuse green, green, spring green, cyan, azure, blue, violet, magenta and rose.
The color wheel can be divided into primary, secondary and tertiary colors.
Primary colors in the RGB color wheel are the colors that, added together, create pure white light. These colors are red, green and blue.
In the RYB color wheel, primary colors are colors that can’t be mixed from other colors. There are three primary colors: red, yellow, and blue.
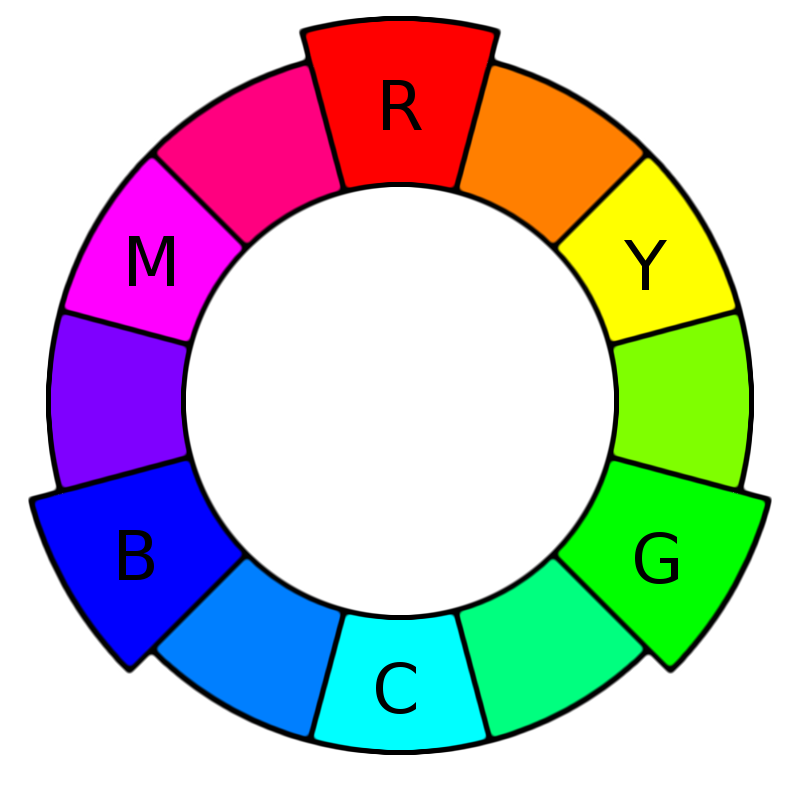 Image by: wtamu.edu
Image by: wtamu.edu
Secondary colors are colors that result from mixing two primary colors. There are three secondary colors. In the RGB color wheel, these are cyan, magenta and yellow. When you mix light, red and green make yellow, green and blue make cyan, and blue and red make magenta.
In the RYB color wheel, the secondary colors are purple (red mixed with blue), orange (red mixed with yellow), and green (yellow mixed with blue).
Tertiary colors are colors made by combining a secondary color with a primary color. There are six tertiary colors. In the RGB color wheel these are orange, chartreuse green, spring green, azure, violet and rose.
In the RYB color wheel, the tertiary colors are red-orange, yellow-orange, yellow-green, blue-green, blue-violet, and red-violet.
2. Color Relationships
Color theory defines different relationships between colors based on their positions on the color wheel:
- Complementary colors: These are colors directly opposite each other on the color wheel. They create high contrast and visual interest when used together.
 Image by: closetomyheart.com
Image by: closetomyheart.com
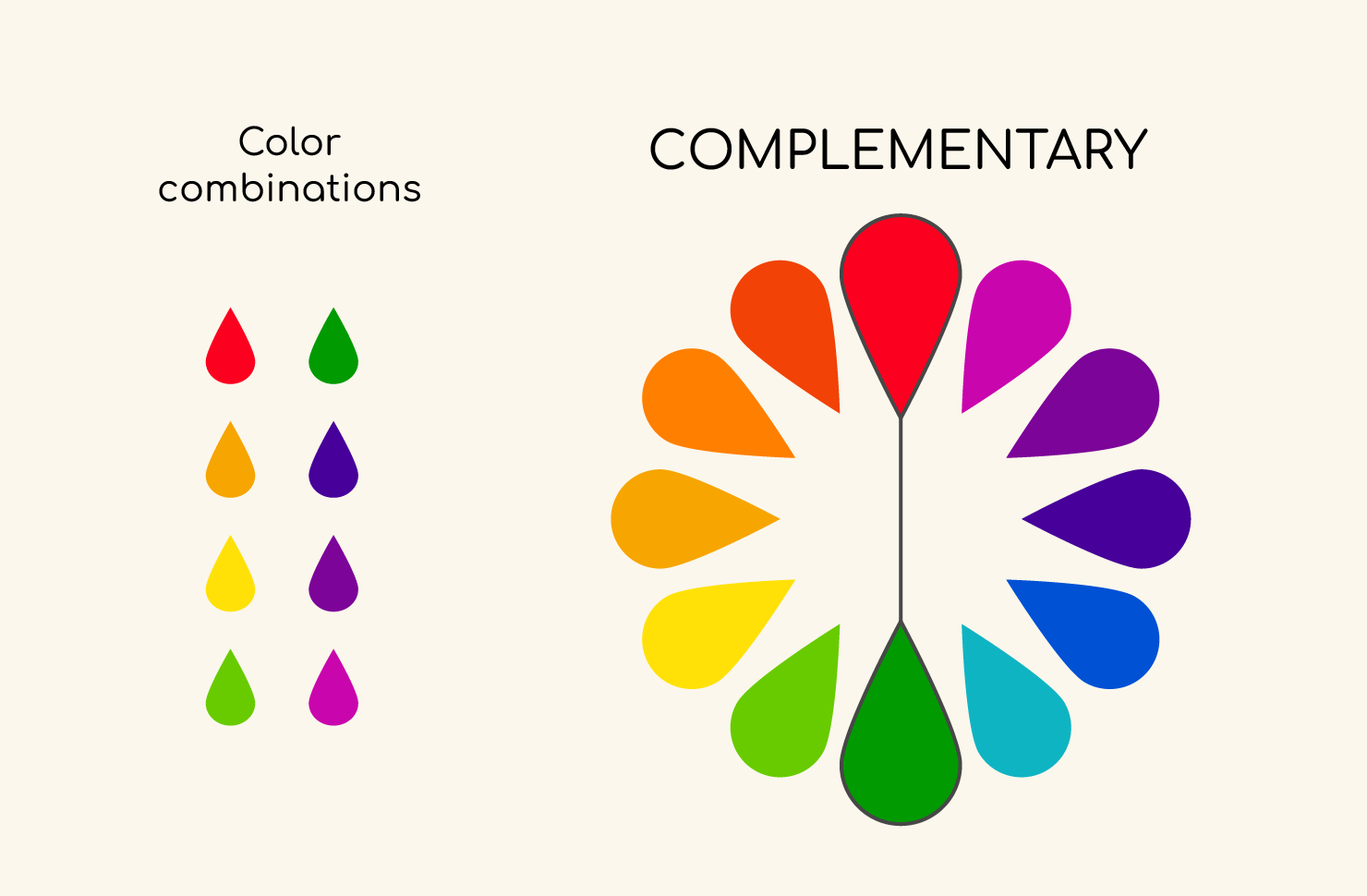 Image source: amadine.com
Image source: amadine.com
- Monochromatic: Three shades, tones and tints of one base color. Provides a subtle and conservative color combination. This is a versatile color combination that is easy to apply to design projects for a
harmonious look.
 Image source: www.canva.com
Image source: www.canva.com
- Analogous colors: These are colors that are next to each other on the color wheel. They create a
harmoniousandcohesivefeeling when used together.
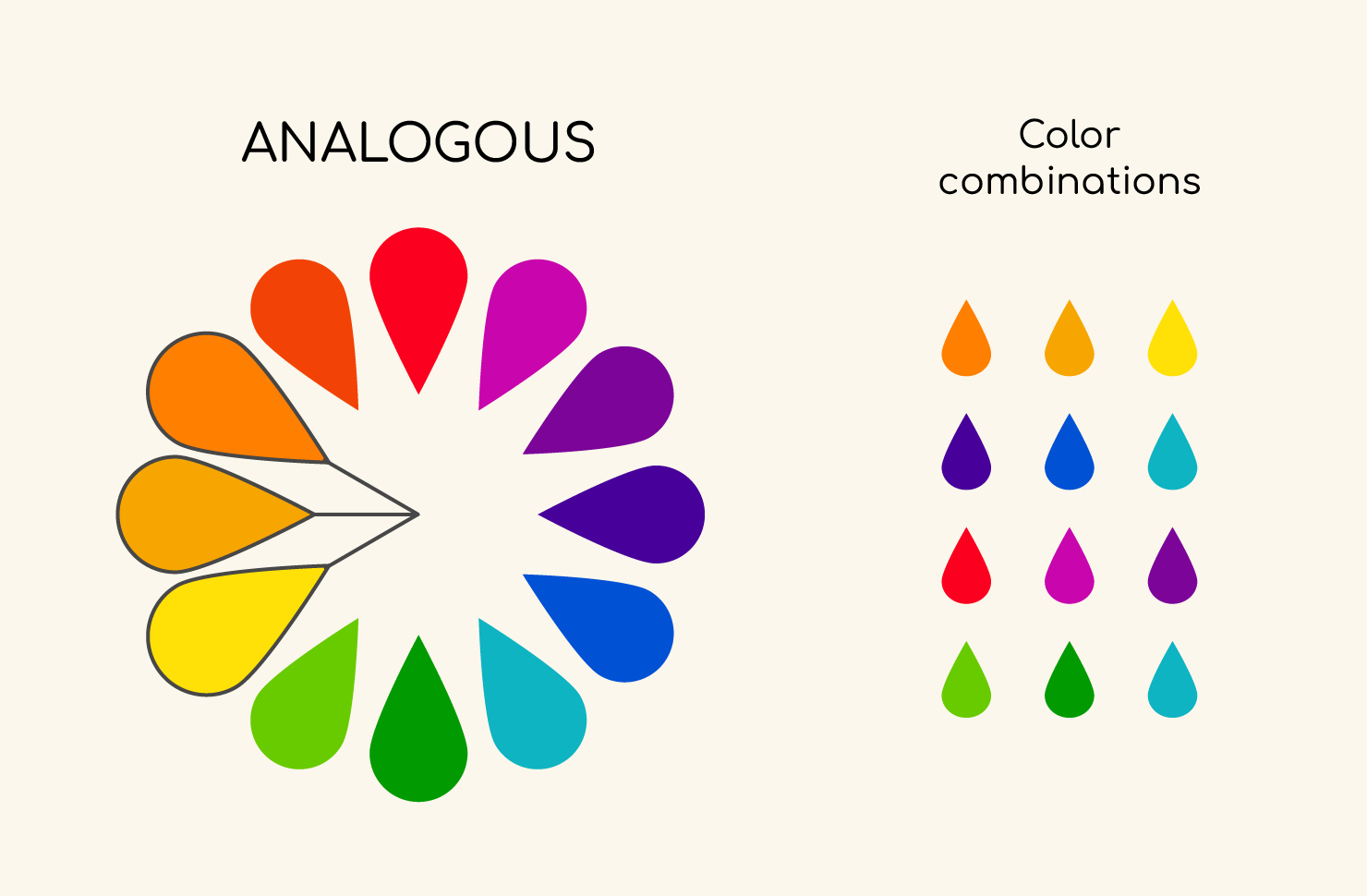 Image by: amadine.com
Image by: amadine.com
- Triadic colors: These are three colors that are evenly spaced on the color wheel. They create a
vibrantanddynamic feelwhen used together. -
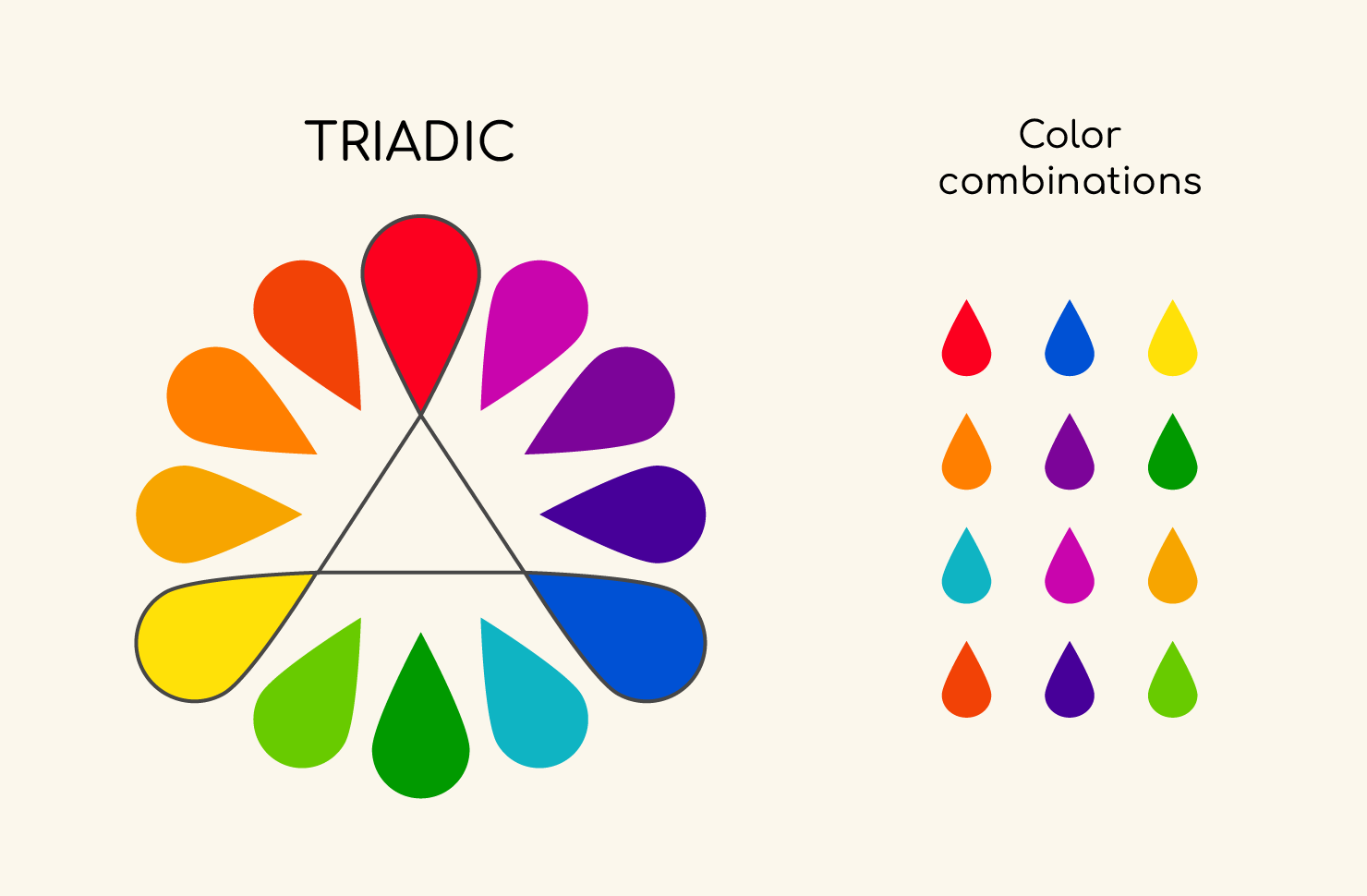 Image by: amadine.com
Image by: amadine.com - Tetradic:
Four colors that are evenly spaced on the color wheel. Tetradic color schemes are bold and work best if you let one color be dominant, and use the others as accents. The more colors you have in your palette, the more difficult it is to balance.
 Image source: www.canva.com
Image source: www.canva.com
2. Warm and cool colors:
Warm colors are the colors from red through to yellow. These colors are said to bring to mind warmth, like the sun.
Cool colors are the colors from blue to green and purple. These colors are said to bring to mind coolness, like water. [2]
 Image by: www.canva.com
Image by: www.canva.com
3. Shades, Tints and Tones:
You can create shades, tints and tones of a color by adding black, grey and white to a base hue.
Shade A shade is created by adding black to a base hue, darkening the color. This creates a deeper, richer color. Shades can be quite dramatic and can be overpowering.
Tint A tint is created by adding white to a base hue, lightening the color. This can make a color less intense, and is useful when balancing more vivid color combinations.
Tones A tone is created by combining black and white—or grey—with a base hue. Like tints, tones are subtler versions of the original color. Tones are less likely to look pastel, and can reveal complexities not apparent in the base color. [2]
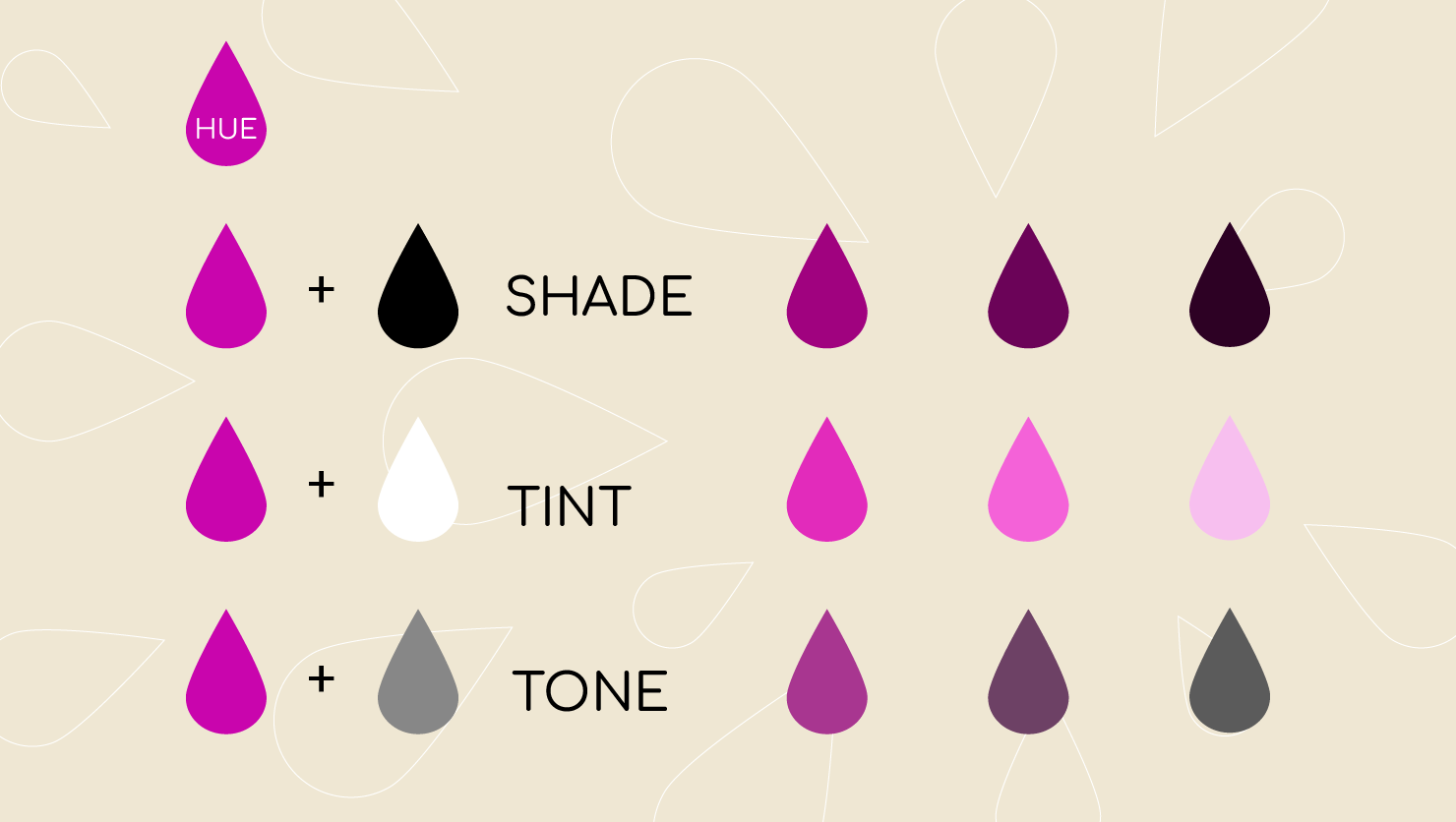 Image by: amadine.com
Image by: amadine.com
CMYK Color Model
- The CMYK color model, also known as the four-color process, is a subtractive color model used in
color printing. - It stands for
Cyan,Magenta,Yellow, andKey (Black). - Unlike the
additive RGB modelused indigital displays, where colors are created by adding different intensities of light, the CMYK model works bysubtractingvarying amounts of light from white to create colors.
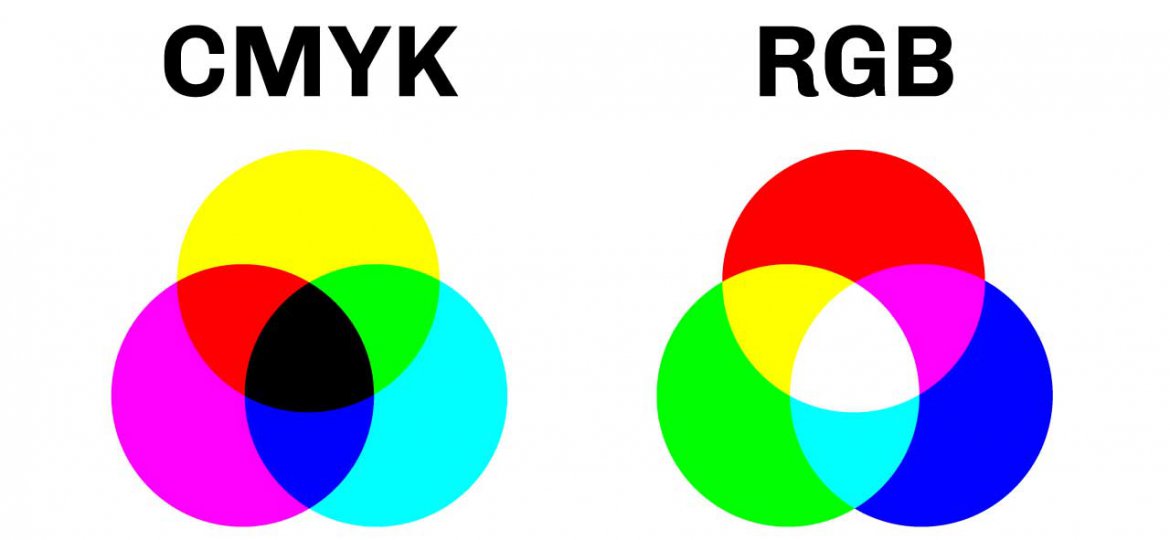 Image source: plumgroveinc.com
Image source: plumgroveinc.com
Subtractive Color Model: White light contains a spectrum of all colors. When light hits an object, some wavelengths are absorbed and others are reflected. The reflected wavelengths determine the color we perceive. In printing, inks work by subtracting specific wavelengths of light.
CMY Inks and Reflected Light:
- Cyan (C): Cyan ink
absorbsred light andreflectsblue and green, creating a cyan color. - Magenta (M): Magenta ink
absorbsgreen light andreflectsblue and red, creating a magenta color. - Yellow (Y): Yellow ink
absorbsblue light andreflectsred and green, creating a yellow color.
Mixing and Matching:
Just like mixing paints, combining CMY inks creates new colors:
- Cyan + Magenta = Blue
- Cyan + Yellow = Green
- Magenta + Yellow = Red
- Combining all three (CMY) creates a dark, muddy color, so…
Black Ink and Limitations: By combining CMY inks, we can create a variety of colors. However, perfect black is difficult to achieve by just subtracting colors. That’s why black (K) is often added as a separate ink in CMYK. This ensures sharp blacks and richer overall colors.
Hue, Saturation and Lightness
- Hue, Saturation, and lightness (HSL) are three fundamental properties used to
describeandmanipulatecolor. - They work together to create the vast spectrum of colors we perceive.
1. Hue:
A hue is basically any color on the color wheel. When you are using a color wheel or a color picker, you can adjust the saturation and luminance of a hue. [2]
2. Saturation:
- Refers to the intensity or purity of the color.
- A highly saturated color is vibrant and bold, while a less saturated color appears muted or washed out.
- Increasing saturation is like adding more pigment to a color, making it richer and more intense. Decreasing saturation makes it closer to
gray. - A saturation of
0%gives you agrayshade, while100%is thefull, rich color.
3. Lightness:
- Represents the brightness or lightness of the color.
- Increasing Lightness makes a color brighter, while decreasing Lightness makes it darker.
- This controls how light or dark the color is.
0% is black,100% is white, and50% is the middle ground.
 Image by: www.canva.com
These three properties are often used in conjunction to represent and manipulate colors in various applications such as:
Image by: www.canva.com
These three properties are often used in conjunction to represent and manipulate colors in various applications such as:
- Image editing software: Programs like Photoshop and Lightroom use HSL sliders to adjust specific colors within an image.
- UI and web design: HSL values can be used to define color schemes for websites and applications.
- 3D graphics and animation: HSL helps create and control color variations in 3D models and animations.
Understanding HSL is crucial for manipulating and working with colors effectively in various creative and technical fields.
Color Psychology
Colors are not just visual elements; they also evoke emotions and associations. Understanding the psychology of color is crucial for using color effectively in various applications. For example:
- Red: Associated with energy, passion, excitement, and danger.
- Yellow: Associated with happiness, optimism, creativity, and caution.
- Blue: Associated with peace, trust, reliability, and sadness.
- Green: Associated with nature, growth, harmony, and freshness.
Applications of Color Theory
Color theory is applied in various fields, including:
- Art and design: Artists and designers use color theory to create visually appealing and meaningful compositions.
- Fashion and interior design: Color choices play a significant role in creating a specific mood and atmosphere in clothing and living spaces.
- Marketing and advertising: Businesses use color to influence consumer behavior and brand perception.
- User interface (UI) design: Color plays a crucial role in making interfaces intuitive and user-friendly.
Typography in Graphic Design
- The power of typography in graphic design
- Exploring different types of fonts and their histories
- Choosing the right font for a project
- Principles of good typography: hierarchy, balance, and readability
Key Terms
- Color Wheel
- Primary Colors
- Secondary Colors
- Complementary Colors
- Warm Colors
- Monochromatic
- Hue
- Saturation
- CMYK Color Model
- Shades, Tints, and Tones
- Subtractive Color Model
- RGB Color Model
- Analogous Colors
- Triadic Colors
- Tetradic Colors
- Color Psychology
- Applications of Color Theory
- Color Theory
True/False (Mark T for True and F for False)
- A tint is created by adding black to a base color.
- Primary colors are red, yellow, and blue in both the RYB and RGB color models.
- Complementary colors sit directly opposite each other on the color wheel and create high contrast.
- Warm colors include blue, green, and purple.
- Monochromatic color schemes use three shades of one base color.
- Mixing cyan and magenta in the RGB color model produces yellow.
- Tertiary colors are created by mixing a primary and a secondary color.
- Adding black to a base hue creates a tint of that color.
- Analogous colors are directly opposite each other on the color wheel.
- Warm colors are typically associated with coolness, like water.
- Secondary colors are created by mixing a primary and a tertiary color.
Answer Key (True/False):
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False (RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue. These are the primary colors in this system, meaning they cannot be created by mixing other colors.)
- True
- False
- False
- False
- False
Multiple Choice (Select the best answer)
Which of the following is NOT a primary color?
- Red
- Green
- Purple
- Yellow
Mixing equal parts of red and yellow creates:
- Orange
- Blue
- Green
- Black
Making a color lighter by adding white creates a:
- Shade
- Tint
- Tone
- Hue
Colors directly opposite each other on the color wheel are called:
- Analogous colors
- Complementary colors
- Tertiary colors
- Warm colors
What is the primary color model used in digital design and printing?
- RGB
- CMYK
- HSV
- Pantone
In the RGB color model, mixing red and green produces which color?
- Blue
- Yellow
- Magenta
- Cyan
In the RGB color model, mixing red and green produces which color?
- Blue
- Yellow
- Magenta
- Cyan
Which property of color refers to the intensity or purity of the color?
- Hue
- Saturation
- Luminance
- Value
The color wheel used in subtractive color mixing (like printing) is:
- RYB (Red, Yellow, Blue)
- RGB (Red, Green, Blue)
- CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black)
- HSL (Hue, Saturation, Luminance)
Which of the following is NOT a primary color according to the RYB color model?
- Red
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
What does CMYK stand for?
- Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key Black
- Cerulean, Maroon, Yellow, Khaki
- Cranberry, Mauve, Yellow, Khol
- Crimson, Magenta, Yellow, Key
CMYK is a color model used primarily for:
- Displaying colors on computer screens
- Creating colors on webpages
- Mixing paints for artistic purposes
- Printing inks for physical media
CMY are considered:
- Primary colors (additive)
- Primary colors (subtractive)
- Secondary colors
- Tertiary colors
Combining equal parts of Cyan, Magenta, and Yellow in CMYK will typically result in:
- Pure white
- A vibrant blue
- A dark brown
- Black (although true black is often achieved with “Key” black)
Why is “Key” black included in CMYK even though mixing CMY can create a dark color?
- To save ink by using less CMY combination
- To achieve deeper, richer blacks than CMY mixing allows
- To represent pure white in printing
- Because black is a primary color in subtractive mixing
HSL stands for:
- Hue, Saturation, Lightness
- Highlighting, Saturation, Luminescence
- Hexadecimal, Saturation, Luminance
- Hue, Shade, Ligh
In HSL, a Lightness value of 0% represents:
- Pure white
- The specific hue at its most vibrant
- Black
- A shade of the chosen hue
Fill in the Blanks
- A ____ is a circular diagram that organizes colors based on their relationships to each other.
- The three primary colors in the traditional RYB color model are ____ , ____ , and ____ .
- ____ colors are created by mixing two primary colors in equal proportions.
- ____ colors are often associated with feelings of warmth and energy, while ____ colors evoke feelings of mind coolness.
Answer Key (Fill in the Blanks):
- color wheel
- red, yellow, blue
- Secondary
- warm, cool
Exercises
Review Questions
RYB, RGB Color Models:
- What is a color wheel, and what does it represent?
- What are primary colors on a color wheel? Can you mix other colors using only primaries?
- How are secondary colors created on a color wheel?
- What does RGB stand for?
- How are different colors created in the RGB model?
- What are some common applications of the RGB color model?
- How are different colors created in the RGB model?
- What does RYB stand for in the RYB color model?
- What are the three primary colors in the RYB model?
- What are the secondary colors formed by mixing primary colors in the RYB model?
- How do the primary colors of the RYB model differ from the primary colors in the RGB model used for light?
- In what field is the RYB color model primarily used?
Color Relationships:
- What is the difference between a warm color and a cool color?
- What are complementary colors? How can you find them on a color wheel?
CMYK:
- What is CMYK Color?
- What does CMYK stand for and explain it?
- Describe the CMY color model used in printing, including the function of each color (CMY) and why black (K) is often added
- Can you describe the relationship between the colors of light absorbed by each ink and the color we perceive in CYMK color model?
- What is Subtractive Color Model?
- Briefly explain the difference between subtractive and additive color models.
- How does CMYK work to create different colors in printing?
- Why is black ink a separate component in CMYK, instead of being created by mixing CMY inks?
HSL
- What is HSL and explain it?
-
What are the three main properties of color: hue, saturation, and value?
- What are the Applications of Color Theory?
- Briefly explain the difference between a shade, tint, and tone.
References and Bibliography
[1] B. Software, “Rules of Color Combination,” amadine.com. https://amadine.com/useful-articles/rules-of-color-combination [2] Canva, “Color wheel - color theory and calculator | canva colors,” Canva’s Design Wiki, 2019. https://www.canva.com/colors/color-wheel/ [3] Adobe, “What are Primary, Secondary & Tertiary Colors? | Adobe,” www.adobe.com. https://www.adobe.com/creativecloud/design/discover/secondary-colors.html [4] C. Baird, “Why are red, yellow, and blue the primary colors in painting but computer screens use red, green, and blue?,” Science Questions with Surprising Answers, Jan. 22, 2015. https://www.wtamu.edu/~cbaird/sq/2015/01/22/why-are-red-yellow-and-blue-the-primary-colors-in-painting-but-computer-screens-use-red-green-and-blue/