Microsoft Word: Paragraph Formatting |Microsoft 365
Microsoft Word: Paragraph Formatting |Microsoft 365
- Download PDF
- To access the updated handouts, please click on the following link: https://yasirbhutta.github.io/ms-word/docs/paragraph-formatting.html
What is Paragraph Formatting
- You can apply paragraph formatting on paragraphs in document.
- A paragraph may be a character, a word, a line or multiple lines.
- Whenever the user presses Enter key, MS Word assumes that it is a next paragraph.
- A paragraph can be identified by paragraph mark ¶
- Only the cursor should be in paragraph to apply formatting.
Automatically Insert Sample Text into a Document:
=RAND()
=RAND(X,Y) where... X= the number of paragraphs you want Y= the number of sentences each paragraph should have
1. Alignment
- Horizontal alignment determines the appearance and orientation of the edges of the paragraph: left-aligned text, right-aligned text centered text, justified text, which is aligned evenly along the left and right margins. For example, in a paragraph that is left-aligned (the most common alignment), the left edge of the paragraph is flush with the left margin.
Types of paragraph alignment:
- Left alignment: Aligns text on left margin. This is the default paragraph alignment.
- Right alignment: Aligns text on the right margin.
- Center alignment: is evenly centered between the left and right margins.
- Justified Alignment: aligns text on both left and right margins. Justified alignment may add spaces between words to extend your text so that it fits between margins.
Left-align, center, right-align, or justify text within a paragraph.
2. Indentation
- Indentation determines the distance of the paragraph from either the left or the right margin. Indent can be set for individual paragraph or a group of paragraphs.
Types of Indents
Left Indent: Move in the left side of the paragraph by certain amount from left page margin. First Line Indent: A first line indent inserts space between the first line and the page margin. Hanging Indent: In which the first line of the paragraph is not indented, but subsequent lines are. Right Indent: Move in the right side of the paragraph by certain amount from right page margin.
Adjust the indentation (left or right) for paragraphs.
- Use Decrease Indent to remove extra space from the left of the entire paragraph.
- Use Increase Indent to add extra space to the left of the entire paragraph.
3. Line and Paragraph Spacing
Adjust the space between lines of text or between paragraphs.
4. Bulleted and Numbered Lists
Create bulleted or numbered lists using the Bulleted List and Numbered List commands.
5. Columns
- A document may begin with a single column format
- Text formatted in Multiple columns occupies more page space than if it is formatted in Single Column
- The white spaces needed between columns takes extra page
- Text presented in a multiple column structure flows from the bottom of the first column to the top of the next column It can be changed to two columns in the middle of the page by applying two column style from that point
Apply Multiple column
On the Page Layout tab, in the Page Setup group, click Column.
Select one choice from Two, Three, Left, Right, More Options
Single & Double Column Text
Shading and Borders:
Apply background color (shading) to a paragraph or selected text. Set borders around selected text, paragraphs, or tables 1.
Paragraph Settings: Access the Paragraph dialog box to configure additional settings such as outline level, tabs, line breaks, and page breaks
2.1 Indenting Paragraph
2.1.1 Indenting Using Ruler 2.1.2. Indent using Paragraph Dialog Box Click in front of the line that you want to indent. On the Page Layout tab, click the Paragraph Dialog Box Launcher, and then click the Indents and Spacing tab.
In the Special list under Indentation, click First line, and then in the By box, set the amount of space that you want the first line to be indented. 2.1.3. Indent using Paragraph group Click in front of the line that you want to indent. On the Page Layout tab, click the Paragraph group will be use to set left and right indent.
Indent Using Keyboard 2.2. Paragraph Alignment
Align Paragraphs using paragraph group Align Paragraphs Shortcut Keys 2.3. Line Spacing in Paragraphs Line Spacing sets the amount of Space between lines within a paragraph. Single spacing is the default Example: Line spacing 2.3 Changing line spacing using paragraph group Select the paragraph for which you want to change the line spacing. On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, click Line Spacing.
Line spacing More options Change Line Spacing Using Keyboard
Drop Cap
- The dropped cap is used to enlarge dropped initial capital letter in paragraph
- It can be used to begin a document or a chapter, or to add interest to a newsletter or invitation.
Apply Drop Cap Click in the paragraph that you want to begin with a drop cap. The paragraph must contain text. On the Insert tab, in the Text group, click Drop Cap.
Click Dropped or In margin.
Bullets and Numbering
- Bullets and Numbering are used to start bulleted and numbered list.
- Bullets and Numbers features have different bullet styles and numbering formats.
Apply Bullets & Numbering Select list/text to apply Bullets or Numbering. On the Home tab, under Paragraph, click the arrow next to Bullets or Numbering.
Click the bullet or numbering list format that you want in the Bullet Library or the Numbering Library.
- Bullet Styles
- Numbering Formats
Multilevel List
- A multilevel list shows the list items at different levels rather than at one level. Multilevel list have different list styles.
Example: Apply Multilevel Numbering Select list/text to apply Multilevel Numbering. On the Home tab, under Paragraph, click the arrow next to Multilevel Numbering.
Click the multilevel numbering list format that you want in the Multilevel Numbering Library.
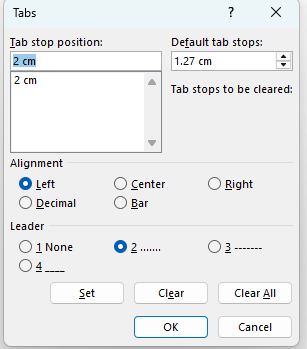
Tabs
- Tab stops are markers that can be used to make parallel columns of text
- Tab stops are set by default at half-inch intervals between the Left and right margins in a document
Tab Key Features
- Default tab stops Specifies amount of spacing that is applied each time you press the TAB key.
- Tab stops to be cleared Displays tab stops that have been marked for deletion from the Tab stop position list. Cleared tabs are deleted from the list when you click OK.
Tab Alignments Left Sets a left start position of text that will then run to the right as you type. Center Sets the position of the middle of the text. The text centers on this position as you type. Right Sets a right start position of text that will then run to the left as you type. Decimal Aligns numbers around a decimal point. Bar Inserts a vertical bar at the tab position. Not used for positioning text.
Tabulated text and Tab marks Example Tabs dialog box Lab Assignment Prepare
Key Terms
True/False (Mark T for True and F for False)
Answer Key (True/False):
Multiple Choice (Select the best answer)
Which of the following is NOT a type of paragraph alignment available in Microsoft Word?
a) Left-aligned b) Centered c) Underlined d) Justified
What is the purpose of indentation in paragraphs?
a) To change the font size b) To control the spacing between lines c) To adjust the distance of the paragraph from the margins d) To create bulleted or numbered lists
What is the default alignment for text in a paragraph in Microsoft Word? A) Right alignment B) Center alignment C) Justified alignment D) Left alignment
How can you remove extra space from the left of an entire paragraph in Microsoft Word? A) Increase Indent B) Decrease Indent C) Line spacing D) Paragraph spacing
What does the “RAND(X,Y)” function in Microsoft Word do? A) Inserts random text into the document B) Inserts random numbers into the document C) Inserts random dates into the document D) Inserts random formulas into the document
1. What is paragraph formatting in Microsoft Word?
A) Formatting applied to the entire document
B) Formatting applied to a paragraph, identified by the ¶ symbol
C) Formatting applied only to headers
D) Formatting applied to the footer
Answer: B) Formatting applied to a paragraph, identified by the ¶ symbol
2. Which of the following automatically inserts sample text into a document?
A) =SUM(X,Y)
B) =TEXT(X,Y)
C) =RAND(X,Y)
D) =SAMPLE(X,Y)
Answer: C) =RAND(X,Y)
3. What is the default paragraph alignment in Microsoft Word?
A) Right alignment
B) Left alignment
C) Center alignment
D) Justified alignment
Answer: B) Left alignment
4. Which alignment ensures text is evenly aligned along both the left and right margins?
A) Left alignment
B) Right alignment
C) Center alignment
D) Justified alignment
Answer: D) Justified alignment
5. What does a “First Line Indent” do?
A) Moves the entire paragraph to the right
B) Indents the first line of the paragraph from the left margin
C) Indents all lines except the first line of the paragraph
D) Moves the entire paragraph to the left
Answer: B) Indents the first line of the paragraph from the left margin
6. How can you adjust line spacing in a paragraph?
A) By using the Font group
B) By using the Line Spacing option in the Paragraph group
C) By changing the document margins
D) By resizing the font
Answer: B) By using the Line Spacing option in the Paragraph group
7. What does a “Hanging Indent” do?
A) Indents the first line of a paragraph
B) Leaves the first line unchanged and indents all subsequent lines
C) Moves the paragraph to the center of the page
D) Adds space to the top of the paragraph
Answer: B) Leaves the first line unchanged and indents all subsequent lines
8. What is the purpose of the “Drop Cap” feature?
A) To reduce the font size of a paragraph
B) To align text to the right margin
C) To enlarge the first letter of a paragraph for decorative purposes
D) To add bullets to a list
Answer: C) To enlarge the first letter of a paragraph for decorative purposes
9. Which of the following tab alignments is used to align numbers around a decimal point?
A) Left alignment
B) Center alignment
C) Right alignment
D) Decimal alignment
Answer: D) Decimal alignment
10. How can you create a multilevel numbered list in Microsoft Word?
A) Use the Bulleted List option
B) Use the Multilevel Numbering option in the Paragraph group
C) Insert multiple columns
D) Use the Tabs dialog box
Answer: B) Use the Multilevel Numbering option in the Paragraph group
11. Which of the following is NOT a type of indent in Microsoft Word?
A) Left Indent
B) Hanging Indent
C) Center Indent
D) First Line Indent
Answer: C) Center Indent
12. Where can you access the Paragraph dialog box in Microsoft Word?
A) Home tab → Font group
B) Insert tab → Text group
C) Page Layout tab → Paragraph group
D) Design tab → Themes group
Answer: C) Page Layout tab → Paragraph group
Let me know if you’d like me to refine or expand these questions further!
Fill in the Blanks
Here are fill-in-the-blank questions based on the provided content for Microsoft Word: Paragraph Formatting:
1. A paragraph in Microsoft Word can be identified by the _______ symbol.
Answer: ¶ (paragraph mark)
2. The default paragraph alignment in Microsoft Word is _______.
Answer: Left alignment
3. The _______ command is used to adjust the distance between the left and right margins of a paragraph.
Answer: Indentation
4. The type of indent where only the first line of the paragraph is indented is called _______.
Answer: First Line Indent
5. The _______ feature adds space between lines of text within a paragraph.
Answer: Line Spacing
6. The _______ feature in Microsoft Word enlarges the first letter of a paragraph for decorative purposes.
Answer: Drop Cap
7. The alignment option that evenly aligns text along both the left and right margins is called _______.
Answer: Justified alignment
8. To create a numbered list, you use the _______ command in the Paragraph group.
Answer: Numbered List
9. The _______ indent leaves the first line unchanged and indents all subsequent lines of a paragraph.
Answer: Hanging Indent
10. Tab stops can be used to create _______ columns of text in a document.
Answer: Parallel
11. In Microsoft Word, the _______ dialog box allows users to configure additional paragraph settings such as tabs, line breaks, and page breaks.
Answer: Paragraph
12. The shortcut key combination to decrease the indentation of a paragraph is _______.
Answer: Decrease Indent
13. To apply multiple columns in a document, go to the _______ tab and select the Columns option.
Answer: Page Layout
14. The _______ option in the Tabs dialog box aligns numbers around a decimal point.
Answer: Decimal alignment
15. When creating a bulleted list, the _______ feature provides different bullet styles.
Answer: Bullets
Let me know if you’d like additional variations or refinements!
Answer Key (Fill in the Blanks):
Exercises
Review Questions
- Describe four common paragraph formatting options in Microsoft Word and explain their uses. Additionally, identify the keyboard shortcuts for the following document management functions: creating a new file, saving, saving as, and closing a document.